WebFOCUS
Online Help > Managed Reporting End User > Visualizing Trends in Reports > Applying Bar Graphs
Vertical or horizontal bar graphs highlight relationships
and trends among data.
-
Vertical Bar Graph. You
can apply a vertical bar graph to report columns associated with
an ACROSS sort field. The report output displays a vertical bar graph
in a new row above the associated data values as shown in the following
image.
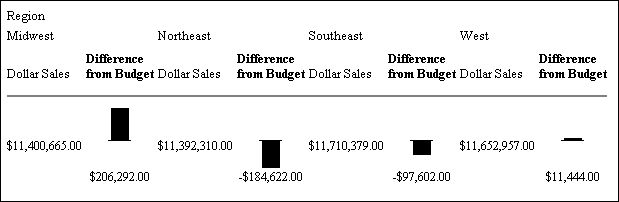
Bar
graphs that project above the zero line represent positive values,
while bar graphs that project below the zero line represent negative
values.
-
Horizontal Bar Graph. You
can apply a horizontal bar graph to report columns. The report output
displays a horizontal bar graph in a new column to the right of
the associated data values as shown in the following image.
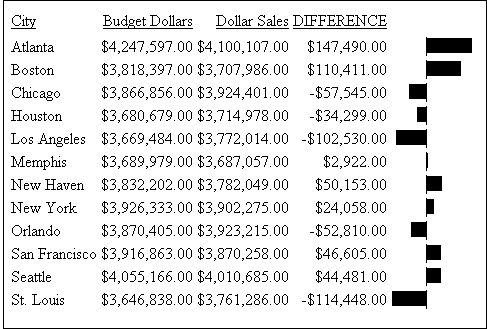
Bar
graphs that project to the right of the zero line represent positive
values, while bar graphs that project to the left of the zero line
represent negative values.
The length of each vertical or horizontal bar graph is proportional
to the magnitude of its associated data value. The shortest bar
graph appears for the value with the minimum magnitude, the longest
bar graph for the value with the maximum magnitude, and bar graphs of
varying length appear for each value within the minimum-maximum
magnitude range. Notice in the figure that a value of 147,490.00
produces a longer horizontal bar graph than a value of 50,153.00.
Therefore, a complete row of vertical bar graphs or a complete column
of horizontal bar graphs forms a bar chart.
You can only apply data visualization bar graphs to numeric report
columns (integer, decimal, floating point single-precision, floating
point double-precision, and packed). Bar graphs applied to alphanumeric,
date, or text field formats are ignored.
You can display data visualization
bar graphs in OLAP-enabled HTML reports, where bar graphs are applied
to Measures.

